MH370 - what happened?
My recommendation to the NTSB
I sent this email to Peter Knudson at the NTSB, and he will consider if its worthy of forwarding onto investigators. I would like feedback on the plausibility.
At the end of this email, I’ve listed sensible and low-cost recommendations to best aid recovery efforts.
Has anyone considered if the below FAA Airworthiness Directive could be a clue the MH370 investigation?
A November 2013 FAA Airworthiness Directive for the 777
http://www.gpo.gov/fdsys/pkg/FR-2013-09-26/html/2013-23456.htm
SUMMARY: We propose to adopt a new airworthiness directive (AD) for
certain The Boeing Company Model 777 airplanes. This proposed AD was
prompted by a report of cracking in the fuselage skin underneath the
satellite communication (SATCOM) antenna adapter. This proposed AD
would require repetitive inspections of the visible fuselage skin and
doubler if installed, for cracking, corrosion, and any indication of
contact of a certain fastener to a bonding jumper, and repair if
necessary. We are proposing this AD to detect and correct cracking and
corrosion in the fuselage skin, which could lead to rapid decompression
and loss of structural integrity of the airplane.
Summary: It’s plausible that a fuselage section near the SATCOM antenna adapter failed, disabling satellite based - GPS, ACARS, and ADS-B/C - communications, and leading to a slow decompression that left all occupants unconscious. If such decompression left the aircraft intact, then the autopilot would have flown the planned route or otherwise maintained its heading/altitude until fuel exhaustion.
A slow decompression (e.g. from a golfball-sized hole) would have gradually impaired and confused the pilots before cabin altitude (pressure) warnings sounded.
Chain of events:
Likely fuselage failure near SATCOM antenna adapter, disabling some or all of GPS, ACARS, ADS-B, and ADS-C antennas and systems.
Thus, only primary radars would detect the plane. Primary radar range is usually less than 100nm, and is generally ineffective at high altitudes.
If the decompression was slow enough, it’s possible the pilots did not realize to put on oxygen masks until it was too late. (See Helios 522)
Also explains why another Pilot thirty minutes ahead heard “mumbling” from MH370 pilots.
(VHF comms would be unaffected by SATCOM equipment failure.)
With incapacitated pilots, the 777 would continue to fly on Autopilot - programmed to maintain cruise altitude and follow the programmed route.
Other thoughts:
The plane was equipped with cellular communication hardware, supplied by AeroMobile, to provide GSM services via satellite. However this is an aftermarket product; it’s not connected through SATCOM (as far as I know).
This explains why 19 families signed a statement alleging they were able to call the MH370 passengers and get their phones to ring, but with no response.
When Malaysian Airlines tried to call the phone numbers a day later, the phones did not ring. By this time, fuel would have been exhausted.
Note: 777 Passenger Oxygen masks do not deploy until cabin altitude reaches 13,500. Passengers were likely already unconscious by then, if it was a slow decompression. No confirmed debris has been found anywhere near the search area, consistent with the plane having flown for hours after it lost radar contact.
Conclusion:
This was likely not an “explosive decompression” or “inflight disintegration.” This was likely a slow decompression that gradually deprived all crew/passengers of oxygen, leaving the autopilot to continue along the route autonomously.
The aircraft may be at the floor of the East China Sea, Sea of Japan, or the Pacific Ocean thousands of miles northeast from the current search zone.
I’ve circled a probable search space in Red on this map; it that assumes that MH370’s autopilot continued along the programmed route.
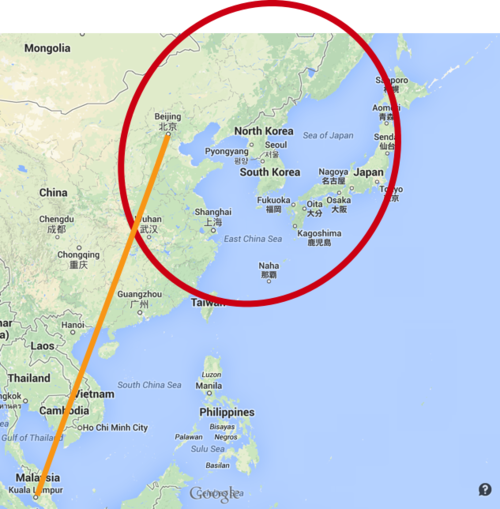
Recommendations:
• Investigators should obtain data logs from primary radars throughout mainland China that would have been along the planned route. They may be the best clue as to the trajectory of the aircraft.
• Investigators should obtain all passengers’ cell phone log and location data. The timing of the last successful cellular connection (ring/SMS/data-packet) can predict how long the plane was in the air. iPhone/iOS location (GPS) data may be available from Apple if subpoenaed. Android location data may be available from Google.
• Add a secondary search space to include a 300nm radius around Beijing, focusing on surrounding bodies of water. Using planned routing trajectory, known autopilot logics, fuel quantities, and weather patterns, it may be possible to define a smaller 50nm * 50nm search space. Consider running the above scenario in MH’s 777-200ER full flight simulator.
• Boeing should provide expertise about the SATCOM antenna schematics and autopilot/navigation logic, so as to help plot this second search space.
Comments
Post a Comment